CULINARY HERBS - COOKING WITH HERBS
PROPAGATION
CUTTINGS
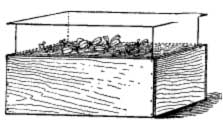
Glass-Covered Propagating Box[Pg 34]
No herbs are so easy to propagate by means of cuttings as spearmint, peppermint, and their relatives which have underground stems. Every joint of these stems will produce a new plant if placed in somewhat moist soil. Often, however, this ability is a disadvantage, because the plants are prone to spread and become a nuisance unless watched. Hence such plants should be placed where they will not have their roots cut by tools used close to them. When they seem to be extending, their borders should be trimmed with a sharp spade pushed vertically full depth into the soil and all the earth beyond the clump thus restricted should be shaken out with a garden fork and the cut pieces of mint removed. Further, the forked-over ground should be hoed every week during the remainder of the season, to destroy lurking plantlets.[Pg 35]
The other perennial and biennial herbs may be readily propagated by means of stem cuttings or "slips," which are generally as easy to manage as verbenas, geraniums and other "house plants." The cuttings may be made of either fully ripened wood of the preceding or the current season, or they may be of firm, not succulent green stems. After trimming off all but a few of the upper leaves, which should be clipped to reduce transpiration, the cuttings - never more than 4 or 5 inches long - should be plunged nearly full depth in well-shaded, rather light, porous, well-drained loam where they should remain undisturbed until they begin to grow. Then they may be transplanted. While in the cutting bed they must never be allowed to become dry. This is especially true of greenwood cuttings made during the summer. These should always have the coolest, shadiest corner in the garden. The cuttings taken in the spring should be set in the garden as soon as rooted; but the summer cuttings, especially if taken late, should generally be left in their beds until the following spring. They may, however, be removed for winter use to window boxes or the greenhouse benches.
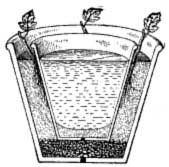
Flower Pot Propagating BedOften the plants grown in window boxes may supply the early cuttings, which may be rooted in the house. Where a greenhouse is available, a few plants may be transplanted in autumn either from the garden or from the bed of summer cuttings just mentioned, kept in a rather cool temperature during the winter and drawn upon for cuttings as the stems become sufficiently mature. The rooting may take place in a regular cutting bench, or it may occur in the soil out of doors, the plantlets being transplanted to pots as soon as they have rooted well.
If a large number of plants is desired, a hotbed may be used in early spring and the plants hardened in cold frames as the season advances. Hardening is essential with all plants grown under glass for outdoor planting, because unless the plants become used to outside temperatures before being planted in the open ground, they will probably suffer setback, if they do not succumb wholly to the unaccustomed conditions. If well managed, however, they should do fine.
Next Page - Propagating by Layers
Culinary Herbs Ebook - Contents